The ICU environment requires specialized skills and attention to critically ill patients․ Nurses play a vital role in providing high-quality, evidence-based care, ensuring patient safety and comfort․
1․1 Overview of ICU Environment
The ICU environment is a specialized area designed for critically ill patients requiring continuous monitoring and advanced life-support interventions․ It is equipped with state-of-the-art technology, including ventilators, monitoring systems, and infusion pumps․ The ICU fosters a team-based approach, with nurses, physicians, and allied health professionals collaborating to deliver personalized care․ The fast-paced, high-acuity setting demands precision, adaptability, and a focus on patient-centered care, balancing advanced interventions with basic nursing practices to optimize outcomes․
1․2 Importance of ICU Nursing
ICU nurses are pivotal in delivering high-intensity care to critically ill patients, managing complex conditions, and operating advanced medical equipment․ Their expertise ensures patient stability, comfort, and safety․ ICU nurses provide compassionate care, addressing both physical and emotional needs, while collaborating with multidisciplinary teams to improve patient outcomes․ Their role is crucial in high-stakes environments, requiring precision, empathy, and a commitment to evidence-based practices that enhance patient recovery and quality of life․

Role and Responsibilities of ICU Nurses
ICU nurses provide critical care to unstable patients, operating advanced equipment, administering medications, and monitoring vital signs․ They ensure precise, patient-centered care in high-acuity settings, collaborating with healthcare teams to optimize outcomes․
2․1 Key Duties in Patient Care
ICU nurses are responsible for continuous monitoring of critically ill patients, ensuring precise administration of medications, and performing complex procedures․ They also provide emotional support to patients and their families, maintaining open communication to address concerns and provide updates on treatment progress․ Additionally, they work closely with other healthcare professionals to develop and implement individualized care plans tailored to each patient’s needs, ensuring comprehensive and compassionate care in high-stress environments․
2․2 Collaboration with Healthcare Teams
Effective collaboration is crucial in the ICU, where nurses work alongside physicians, respiratory therapists, and other specialists to provide coordinated care․ Clear communication ensures seamless integration of patient assessments, treatment plans, and interventions․ Nurses actively participate in multidisciplinary rounds, contributing valuable insights on patient status and care needs․ This teamwork fosters a unified approach, enhancing patient outcomes and optimizing resource utilization in the high-stakes ICU environment․
Essential Skills for ICU Nurses
ICU nurses must possess critical thinking, technical proficiency, and effective communication․ Adaptability, attention to detail, and ability to work under pressure are also crucial in this demanding environment․
3․1 Critical Thinking and Decision-Making
Critical thinking is essential for ICU nurses to quickly assess patient conditions and make sound decisions․ They must analyze complex data, prioritize actions, and anticipate potential complications․ Effective decision-making ensures timely interventions, optimizing patient outcomes․ Nurses should stay updated on evidence-based practices and collaborate with healthcare teams to enhance their critical thinking skills․
3․2 Proficiency in Technical Skills
ICU nurses must master technical skills to operate life-saving equipment like ventilators, monitors, and infusion pumps․ Proficiency in these devices ensures accurate patient care and safety․ Nurses should understand how to troubleshoot equipment and maintain proper function․ Technical skills are critical for administering medications, managing lines, and performing procedures․ Staying updated on emerging technologies and evidence-based practices is essential for providing optimal care in the dynamic ICU environment․
3․3 Effective Communication Techniques
Effective communication is crucial in the ICU, where clear and concise interactions ensure patient safety and team collaboration․ Nurses must practice active listening, clarify information, and use empathetic language to comfort patients and families․ Regular updates and shared decision-making foster trust and coordination among healthcare providers․ Non-verbal cues and cultural sensitivity are equally important․ Clear documentation and handoffs prevent errors, ensuring seamless care․ Strong communication skills are vital for managing critical situations and delivering patient-centered care in high-stakes environments․
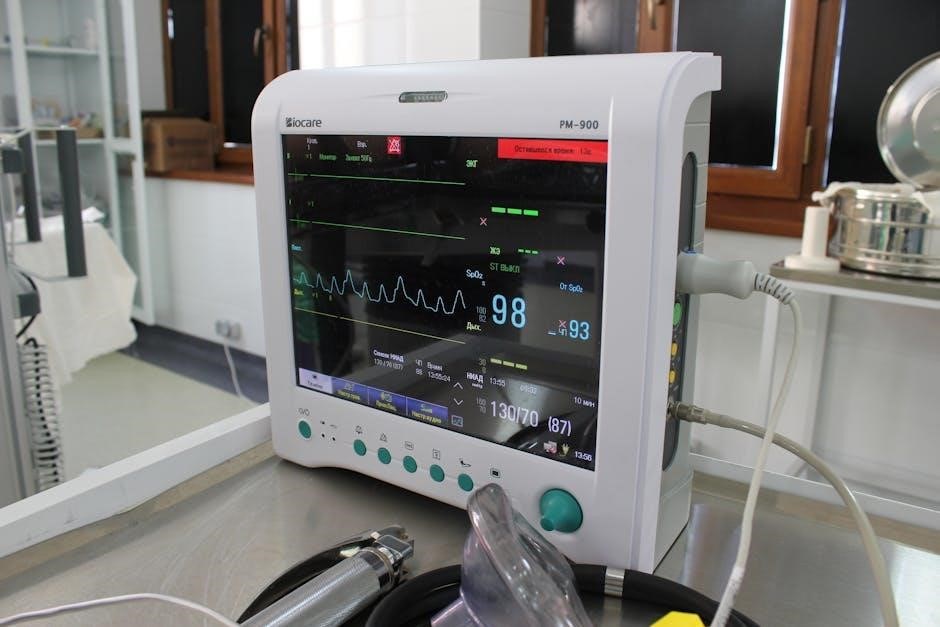
Common ICU Equipment
ICU equipment includes ventilators for respiratory support, monitors for vital signs, and infusion pumps for medication delivery, ensuring precise and life-sustaining care for critically ill patients․
4․1 Ventilators and Respiratory Support
Ventilators are essential for patients with respiratory failure, providing mechanical breathing support․ They maintain oxygenation and carbon dioxide removal, with settings like tidal volume and PEEP tailored to patient needs․ Non-invasive options like CPAP or BiPAP are used for less severe cases․ Monitoring ventilator settings and patient response is critical to ensure effective support and prevent complications such as barotrauma or lung injury․ Proper management of respiratory support is vital for improving patient outcomes in the ICU․
4․2 Monitoring Devices and Sensors
Monitoring devices in the ICU, such as ECG, pulse oximetry (SpO2), and invasive blood pressure monitors, provide real-time data on patient vital signs․ These tools enable nurses to quickly identify and respond to changes in a patient’s condition․ Sensors are used to track oxygen saturation, heart rate, and respiratory rate, while advanced systems monitor neurological activity․ Accurate and continuous monitoring ensures timely interventions and enhances patient safety and outcomes in critical care settings․
4․3 Infusion Pumps and IV Management
Infusion pumps are essential for precise IV medication and fluid delivery in the ICU․ These devices allow nurses to set exact administration rates, reducing errors․ IV management involves maintaining catheter patency, preventing infections, and monitoring for complications․ Nurses must ensure compatibility of solutions and medications, as well as regularly assess IV sites for signs of phlebitis or infiltration․ Proper use of infusion pumps and IV lines is critical for patient safety and therapeutic effectiveness in critical care settings․

Patient Assessment and Monitoring
Patient assessment and monitoring in the ICU involve continuous evaluation of critical conditions, utilizing advanced technology and clinical skills to ensure timely interventions and optimal care outcomes․
5․1 Basic Assessment Techniques
Basic assessment techniques in the ICU include systematic evaluations of airway, breathing, and circulation (ABCs)․ Nurses perform regular head-to-toe exams, monitor vital signs, and utilize tools like ECG and oxygen saturation to identify deviations from baseline․ These techniques ensure early detection of complications, enabling prompt interventions and maintaining patient stability․ Proper documentation and communication of findings are crucial for comprehensive care planning and effective team collaboration in critical settings․
5․2 Interpretation of Vital Signs
Interpreting vital signs is critical in the ICU․ Nurses monitor heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, oxygen saturation, and temperature to assess patient stability․ Abnormal readings, such as tachycardia or hypoxia, indicate potential complications․ Understanding these trends helps guide interventions, like adjusting oxygen therapy or fluid administration․ Accurate interpretation ensures timely responses, preventing escalation of critical conditions and promoting optimal patient outcomes in high-acuity settings․
5․3 Frequency and Documentation
Documentation in the ICU is crucial for continuity of care․ Nurses must record vital signs, interventions, and patient responses frequently, typically every 1-4 hours․ Accurate and timely documentation ensures clear communication among the healthcare team․ Electronic health records are commonly used for consistency and accessibility․ Regular updates help track patient progress and guide future care decisions, supporting patient safety and legal accountability․ Consistent documentation practices are essential for high-quality, patient-centered care in critical settings․

Medications in the ICU
Medications in the ICU are critical for managing life-threatening conditions․ Common drugs include sedatives, analgesics, antibiotics, and vasoactive agents․ Safe administration and monitoring are essential to prevent adverse effects․
6․1 Commonly Used Drugs
In the ICU, commonly used drugs include sedatives like propofol, analgesics such as fentanyl, and antibiotics like meropenem․ Vasoactive agents, including norepinephrine, are used to manage blood pressure, while neuromuscular blockers assist in mechanical ventilation․ These medications are essential for stabilizing critically ill patients and ensuring proper organ function․ Nurses must administer these drugs carefully, adhering to strict protocols to avoid complications and ensure patient safety․
6․2 Safe Administration Practices
Safe drug administration in the ICU requires verifying orders, using barcode scanning, and ensuring the right dose, route, and timing․ Nurses must double-check high-alert medications and be vigilant for potential errors․ Continuous patient monitoring during and after administration is crucial․ Adherence to hospital protocols and clear documentation are essential to prevent adverse events and ensure patient safety․ Open communication with the healthcare team further enhances the reliability of medication administration in critical care settings․
6․3 Monitoring for Side Effects
Monitoring for side effects in the ICU involves continuous vigilance and regular assessments․ Nurses must observe for adverse reactions, such as respiratory changes or neurological alterations․ Vital signs and lab results should be reviewed frequently․ Documentation of any abnormalities is crucial, and prompt intervention is necessary to mitigate harm․ Effective communication with the healthcare team ensures timely adjustments to treatment, prioritizing patient safety and minimizing complications in critically ill patients․
Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration are crucial in the ICU, ensuring seamless teamwork among healthcare professionals and clear understanding for patients and their families․
7․1 Effective Communication Strategies
Effective communication in the ICU involves clear, concise, and empathetic interactions․ Nurses should use active listening, maintain eye contact, and ensure understanding․ Utilizing structured communication tools like SBAR (Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation) enhances clarity․ Regular updates to patients and families build trust․ Non-verbal cues and cultural sensitivity are also crucial․ Documentation should be accurate and timely to ensure continuity of care․ Clear communication fosters collaboration and improves patient outcomes in critical care settings․
7․2 Interdisciplinary Teamwork
Interdisciplinary teamwork is crucial in the ICU, where nurses collaborate with physicians, respiratory therapists, and other specialists․ Effective teamwork ensures comprehensive patient care, improves outcomes, and enhances efficiency․ Open communication, mutual respect, and defined roles are essential․ Nurses play a central role in coordinating care and advocating for patients․ Regular team meetings and shared decision-making foster a collaborative environment, ensuring all aspects of patient needs are addressed promptly and effectively․
7․3 Patient and Family Interaction
Effective communication with patients and their families is essential in the ICU․ Nurses provide emotional support, explain treatments, and involve families in care decisions․ Clear updates on patient conditions and prognosis build trust․ Cultural sensitivity and empathy are vital․ Families often feel overwhelmed, so nurses play a key role in reassuring them and addressing their concerns․ This interaction fosters a supportive environment, ensuring patients and families feel informed and involved in care․

Ethical Considerations
ICU nurses face ethical challenges, including end-of-life decisions, patient autonomy, and consent․ Addressing these dilemmas requires a balance of compassion, legal standards, and patient-centered care․
8․1 End-of-Life Care Decisions
End-of-life care decisions in the ICU involve complex ethical considerations․ Nurses play a critical role in supporting families and patients during these difficult times, ensuring dignity and compassion․ Collaboration with healthcare teams is essential to align decisions with patient values and medical realities․ These decisions often require balancing quality of life, medical futility, and patient autonomy․ Nurses must navigate emotional and ethical challenges while adhering to hospital policies and legal guidelines․
8․2 Patient Autonomy and Consent

Patient autonomy is a cornerstone of ethical care in the ICU․ Nurses must respect patients’ rights to make informed decisions about their treatment․ This includes ensuring patients or their surrogates understand their options and provide consent․ Advance directives and healthcare proxies are vital tools for honoring patients’ wishes․ Nurses play a key role in facilitating these discussions and advocating for patients’ autonomy, even in complex or critical situations․ Collaboration with families and healthcare teams ensures ethical and patient-centered care․
8․3 Ethical Dilemmas in ICU
Ethical dilemmas in the ICU often arise from complex decisions involving life-sustaining treatments, resource allocation, and end-of-life care․ Nurses frequently encounter challenges such as balancing patient autonomy with medical advice, managing scarce resources, and addressing moral distress․ These situations require a structured approach, ethical frameworks, and collaboration with interdisciplinary teams to ensure decisions align with patient values and ethical principles․ Open communication and empathy are crucial in navigating these difficult scenarios while maintaining patient-centered care․

Resources for Continued Learning
Recommended textbooks like AACN Essentials of Critical Care Nursing and The Little ICU Book offer in-depth knowledge․ Online courses and professional organizations provide ongoing education and skill enhancement for nurses․
9․1 Recommended Textbooks and Guides
AACN Essentials of Critical Care Nursing and The Little ICU Book are highly recommended for in-depth knowledge․ These resources cover critical care practices, patient assessment, and advanced nursing skills․ The AACN Pocket Handbook provides quick access to essential guidelines․ Additionally, ICU Manual Handbook offers practical insights for daily patient care․ These guides are invaluable for nurses seeking to enhance their expertise in intensive care settings and stay updated with evidence-based practices․
9․2 Online Courses and Tutorials
Online platforms offer diverse learning opportunities for ICU nurses, such as AACN’s Tele-ICU Nursing Practice Guidelines and critical care tutorials․ The ICU Manual Handbook provides interactive modules for enhanced understanding․ Websites like NursesNote and professional organizations offer courses on critical care basics, patient assessment, and advanced life support․ These resources are designed to improve clinical skills, stay updated on best practices, and support continuous professional development in intensive care nursing․
9․3 Professional Organizations
Professional organizations like the American Association of Critical Care Nurses (AACN) and the Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) provide essential resources for ICU nurses․ These organizations offer evidence-based guidelines, educational materials, and networking opportunities․ They also advocate for best practices in critical care nursing, helping professionals stay updated on the latest advancements․ Membership benefits include access to journals, webinars, and conferences, fostering continuous learning and professional growth in the ICU nursing field․
10․1 Summary of Key Points
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of ICU basics, emphasizing the critical role of nurses in delivering high-quality care․ Key topics include the ICU environment, patient assessment, essential skills, common equipment, medications, and ethical considerations․ Effective communication and collaboration with healthcare teams are highlighted as vital for patient outcomes․ Continuous learning and professional development are encouraged to stay updated on best practices in critical care nursing, ensuring optimal patient care and improved clinical outcomes․
10․2 Encouragement for Ongoing Education
Continuous learning is essential for ICU nurses to stay updated on best practices and advancements in critical care․ Encouraging ongoing education through textbooks, online courses, and professional organizations ensures nurses remain proficient in delivering high-quality patient care․ Engaging in lifelong learning fosters professional growth, enhances clinical skills, and contributes to improved patient outcomes․ Nurses are urged to pursue additional training and certifications to stay ahead in this dynamic field․